Convention on the Rights of the Child: Key Takeaways
Explore the Convention on the Rights of the Child, its guiding principles, and how it shapes global child welfare and sponsorship programs.

The Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) is the most ratified human rights treaty globally, recognizing children as individuals with their own rights. Adopted by the UN in 1989 and effective since 1990, it outlines protections across civil, political, economic, social, and cultural areas. The CRC's four guiding principles are:
- Non-discrimination: All children are entitled to equal rights regardless of background.
- Best interests of the child: Decisions affecting children must prioritize their well-being.
- Right to life, survival, and development: Focus on providing basic needs and opportunities for growth.
- Respect for the child’s views: Children have the right to express opinions on matters affecting them.
The CRC also includes protections against child labor under Article 32, requiring measures like minimum age rules, work condition regulations, and penalties for exploitation. By August 2025, 196 countries have ratified the CRC, making it a framework for global child welfare policies. However, challenges in implementation persist, particularly in ensuring regional compliance and awareness.
Nonprofits and programs supporting children, such as sponsorship initiatives, are guided by CRC principles to ensure ethical operations. This includes policies to avoid exploitation, promote financial transparency, and focus on community-wide development rather than individual aid. Tools like HelpYouSponsor assist organizations in aligning with CRC standards by offering controlled communication, transparent reporting, and community-focused fundraising.
Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC)
Core Principles and Rights in the CRC
The CRC (Convention on the Rights of the Child) lays out essential rights and protections that every child deserves. At its heart are four guiding principles that shape how governments, organizations, and communities should treat children.
4 Key Principles of the CRC
Non-discrimination is the cornerstone of the CRC, guaranteeing that every child enjoys their rights, no matter their background. This principle explicitly prohibits discrimination based on factors like race, gender, language, religion, disability, or socioeconomic status. For instance, it ensures that children from low-income families or those with disabilities have the same access to education, healthcare, and social services as anyone else.
The best interests of the child principle ensures that any decision affecting children prioritizes their well-being above all else. This idea has influenced legal systems worldwide, guiding decisions in areas such as family court custody cases and the allocation of public resources for children. Whether it’s planning community programs or funding schools, decision-makers are urged to always put children’s needs first.
The right to life, survival, and development goes beyond ensuring basic necessities like food, shelter, and healthcare. It also emphasizes creating opportunities for education and personal growth, helping children achieve their full potential in life.
Respect for the views of the child recognizes that children have a right to voice their opinions on matters that affect them. This principle encourages listening to children and giving their opinions appropriate consideration based on their age and maturity. It ensures that children are active participants in decisions that shape their lives.
These principles don’t operate in isolation - they work together. For example, when deciding what’s in a child’s best interest, it’s essential to hear the child’s perspective, ensure they aren’t discriminated against, and support their overall growth. Together, these principles form the foundation of child welfare policies and practices worldwide.
Child Labor Protections in the CRC
The Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) emphasizes shielding children from economic exploitation. This commitment ensures that children's safety, education, and overall well-being remain a priority. It also lays the groundwork for protecting other rights outlined in the CRC.
Article 32: Protection from Economic Exploitation
Article 32 specifically addresses the need to protect children from harmful labor practices. It highlights the obligation to shield children from work that could jeopardize their education, health, or development. The Convention states:
"States Parties recognize the right of the child to be protected from economic exploitation and from performing any work that is likely to be hazardous or to interfere with the child's education, or to be harmful to the child's health or physical, mental, spiritual, moral or social development."
To enforce this, States Parties are required to adopt a range of measures, including legislative, administrative, social, and educational actions:
"States Parties shall take legislative, administrative, social and educational measures to ensure the implementation of the present article. To this end, and having regard to the relevant provisions of other international instruments, States Parties shall: (a) Provide for a minimum age or minimum ages for admissions to employment; (b) Provide for appropriate regulation of the hours and conditions of employment; (c) Provide for appropriate penalties or other sanctions to ensure the effective enforcement of the present article."
This framework translates into practical policies such as:
- Setting a minimum age for employment.
- Regulating work hours and conditions.
- Enforcing penalties or sanctions to ensure compliance.
These measures create a robust system to combat child labor and protect children from exploitation.
Global Adoption and Implementation of the CRC
CRC Ratification Worldwide
The CRC has achieved remarkable global reach, underscoring its importance in advancing children's welfare. By August 18, 2025, a total of 196 countries had ratified the CRC, making it the most widely embraced human rights treaty in history. This overwhelming ratification reflects a shared global dedication to creating a unified ethical and legal foundation for protecting children's rights across diverse regions and cultures.
CRC Guidelines for Child Sponsorship Programs
Meeting CRC Standards in Sponsorship Programs
Child sponsorship programs must align with CRC (Convention on the Rights of the Child) standards to operate ethically. In 2018 alone, evangelical organizations raised over $944 million to support child welfare programs through sponsorships, highlighting the vast scale and responsibility these efforts carry.
To comply with CRC principles, sponsorship programs must adopt robust child protection policies. These policies should safeguard children against exploitation and ensure their voices are included in decision-making processes. Programs are also expected to enforce strict protective measures, maintain financial transparency, and adhere to ethical communication practices to meet international standards.
A growing trend in sponsorship programs is the move toward community-wide development models. This shift recognizes that focusing on individual children can unintentionally create inequalities within communities. Programs grounded in CRC principles now prioritize interventions that benefit families and entire communities, addressing systemic issues and ensuring no child feels excluded.
Policies regarding gifts and additional contributions are another critical aspect of CRC compliance. Thoughtful guidelines prevent disruptions to local economies and avoid fostering favoritism among children in the same community. By doing so, these programs strengthen social cohesion rather than undermining it.
These guidelines form the foundation for how HelpYouSponsor supports CRC compliance.
How HelpYouSponsor Supports CRC Compliance
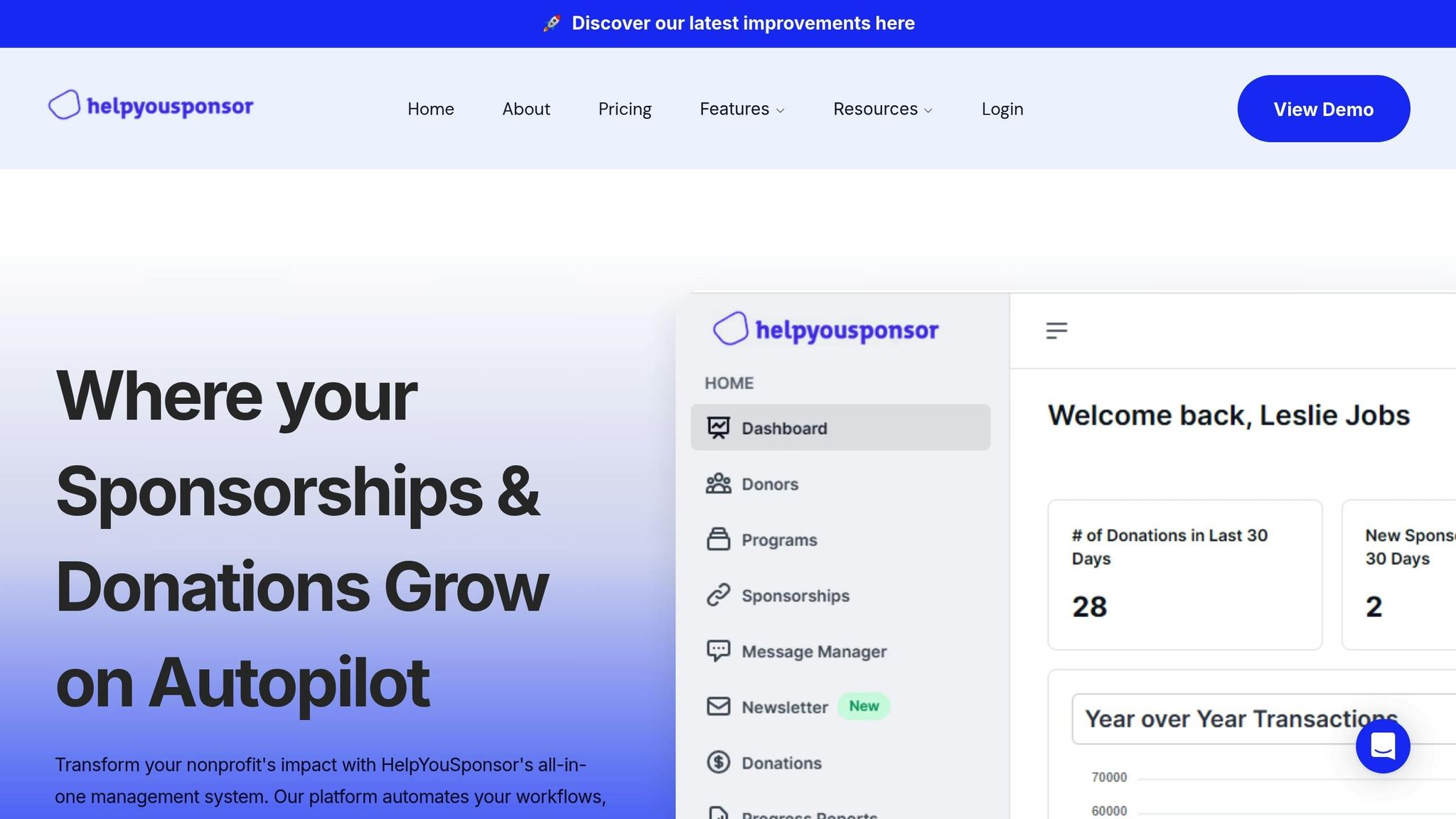
HelpYouSponsor builds on CRC compliance principles by offering practical tools and features designed to uphold ethical and child-focused practices. The platform’s approach aligns with the CRC’s emphasis on child rights, ethical operations, and transparency.
One of its standout features is a donor management system that tracks interactions between sponsors and children. This ensures all communications comply with child protection standards, prioritizing participant safety.
HelpYouSponsor also supports community-focused development by enabling targeted fundraising efforts. Organizations can create campaigns for initiatives like school construction, healthcare programs, or family support services - projects that benefit entire communities rather than singling out individual children. This model helps prevent exclusion and inequality, aligning with CRC values.
The platform provides detailed reporting tools to meet funding transparency requirements. Organizations can generate reports showing exactly how funds are allocated, reinforcing financial accountability. Additionally, automated receipts and thank-you messages keep sponsors informed about program impacts while maintaining appropriate boundaries.
Another key feature is controlled communication. HelpYouSponsor’s tools ensure that updates about community progress are shared without compromising children’s privacy. This approach keeps sponsors engaged while protecting vulnerable participants.
To make compliance accessible for organizations of all sizes, HelpYouSponsor offers scalable pricing options. Its payment gateway integration further supports financial transparency by providing clear transaction records and automating reporting processes. This not only demonstrates financial integrity but also reduces administrative burdens, allowing resources to focus on direct services for children.
HelpYouSponsor’s integrated tools make it easier for organizations to uphold CRC standards while delivering meaningful, community-centered support.
Key Takeaways from the CRC
The Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) sets the foundation for global child welfare, shaping how nonprofits design and carry out their programs to protect children.
At its core, the CRC is built on four guiding principles: non-discrimination, acting in the best interests of the child, ensuring the right to life and development, and respecting children's opinions. These principles are critical in combating child labor, as outlined in Article 32.
For nonprofit sponsorship programs, the CRC acts as both a moral framework and a practical roadmap. By focusing on equality, many modern programs now prioritize community-wide development instead of addressing individual cases. This shift aligns with CRC recommendations for ethical sponsorship practices, ensuring systemic issues are tackled at their roots.
Financial transparency and accountability are also key to adhering to CRC standards. Nonprofits must clearly outline how funds are used, maintain ethical communication, and implement strict child protection policies. These steps not only promote trust but also help address the challenges of enforcing CRC principles across different regions.
Regional enforcement inconsistencies remain a challenge, but technology is stepping in to bridge the gaps. Platforms like HelpYouSponsor integrate CRC principles into their operations by enabling controlled communication, offering transparent reporting, and focusing on community-driven fundraising. These tools help organizations meet international standards while staying true to the CRC's mission.
As the world evolves, the CRC continues to serve as a critical guide for sponsorship programs, ensuring they genuinely work in the best interests of children.
FAQs
How does the Convention on the Rights of the Child protect children from labor exploitation?
The Convention on the Rights of the Child and Child Labor Protections
The Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) takes a firm stand against child labor through Article 32, which protects children from economic exploitation and hazardous work environments. This article obligates countries to set minimum age requirements for employment, ensure safe working conditions, and implement penalties to deter violations.
Beyond these protections, the CRC highlights the importance of a multi-faceted approach. It calls for robust legal frameworks, effective enforcement systems, and proactive initiatives to address child labor while prioritizing children’s overall well-being on a global scale.
What are the main challenges in enforcing the Convention on the Rights of the Child worldwide, and how can they be overcome?
Implementing the Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) on a global scale comes with its fair share of hurdles. Among the most pressing are political disagreements, limited resources, cultural differences, and ineffective enforcement mechanisms. These obstacles often result in uneven protection of children's rights across nations.
To tackle these challenges, countries can focus on reinforcing their legal systems, fostering political will, and promoting international cooperation. Establishing robust monitoring systems - like those overseen by the UN Committee on the Rights of the Child - plays a key role in ensuring adherence to the CRC and safeguarding children's rights. Through these collective efforts, we can work toward a fairer and more nurturing world for all children.
How do sponsorship programs support the goals of the Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) by focusing on community development?
Sponsorship programs resonate with the principles of the Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) by focusing on improving entire communities rather than providing aid to just a few individuals. Instead of singling out specific children, these programs aim to address the broader needs of communities, ensuring that resources benefit children, their families, and the community as a whole.
By fostering collaboration among local stakeholders and investing in long-term solutions, sponsorship programs help communities build resilience and self-reliance. This approach aligns with the CRC’s focus on inclusive development, promoting shared responsibility and creating meaningful, lasting change.

